Engagement and Retention
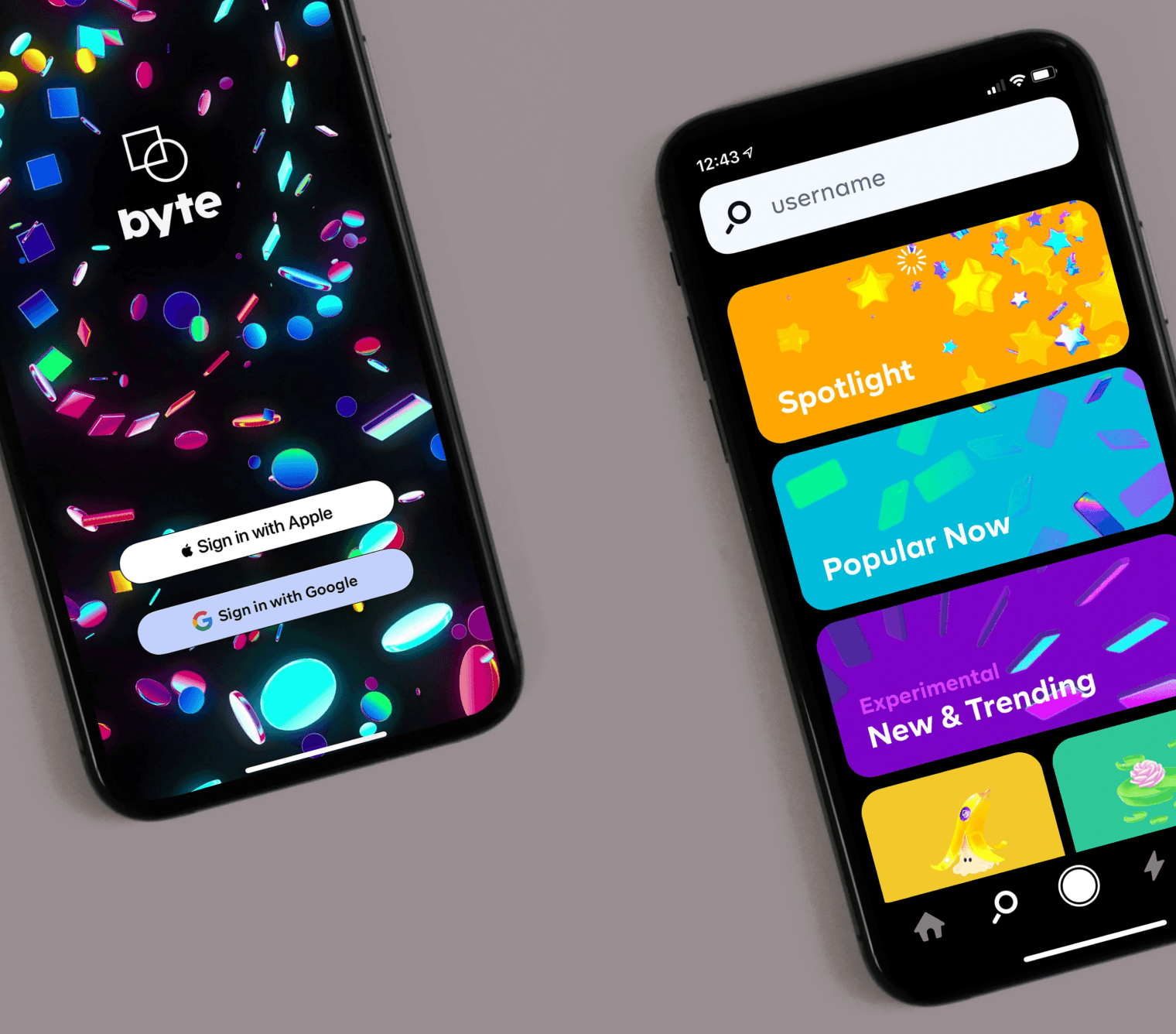
Thoughtfully designed animations captivate users' attention and encourage exploration. Entertaining loading animations, interactive elements, and delightful transitions create memorable experiences that keep users engaged and coming back for more. Visual Hierarchy and Context in animations help establish visual hierarchy and context within the interface. Elements that appear, disappear, or transform with animation convey their importance and relationship to other elements, improving comprehension and usability. Storytelling and Narrative in animation can be used to tell a story or guide users through a narrative journey. From onboarding sequences to interactive tutorials, animations can convey information in a compelling and engaging manner, enhancing user understanding and retention.
Encouragement
Animation design encompasses the creation and implementation of motion graphics, transitions, and effects within digital interfaces or multimedia content. Here's a breakdown of the key elements involved in animation design. Storyboarding - Before diving into animation creation, it's essential to outline the sequence of events or interactions. Storyboarding involves sketching out each scene or step to visualize the flow of the animation, including key actions, transitions, and timing. Motion Principles - understanding the principles of motion is crucial for creating fluid and compelling animations. Principles such as timing, easing, anticipation, and follow-through dictate how objects move and interact, adding realism and impact to animations.
Visual Design - Animation design starts with visual elements such as characters, objects, and backgrounds. These elements should be designed with motion in mind, considering factors like shape, color, texture, and composition to ensure they translate well into animation. Animation Software - Various animation software tools are available to create and edit animations, ranging from beginner-friendly applications to advanced professional software. Popular options include Adobe After Effects, Autodesk Maya, Cinema 4D, and Blender. Keyframes and Timelines - Animation involves setting keyframes to define the starting and ending points of motion, as well as the timing and trajectory in between. Timelines allow animators to organize keyframes and control the sequence and duration of animations.
Transitions and Effects: Animations can be used to create smooth transitions between different states or screens within a UI, enhancing user experience and visual continuity. Effects such as fades, wipes, and overlays can also add visual interest and context to animations. Interaction Design: Animation design in UIs involves creating interactive animations that respond to user input or gestures. These animations should be intuitive, providing feedback, guidance, and visual cues to enhance usability and engagement.
Performance Optimization: Optimizing animations for performance is essential, especially in web and mobile applications where resources may be limited. Techniques such as using CSS animations, optimizing file sizes, and minimizing the number of animations can help maintain smooth performance. Testing and Iteration: Like any design process, animation design requires testing and iteration to ensure effectiveness and usability. Soliciting feedback from users and stakeholders and conducting usability testing can help identify areas for improvement and refinement.
Animation design is a dynamic and creative process that requires a combination of technical skill, artistic vision, and user-centered design principles. By carefully crafting animations that enhance user experience, convey information effectively, and evoke emotion, animators can create compelling and immersive digital experiences.